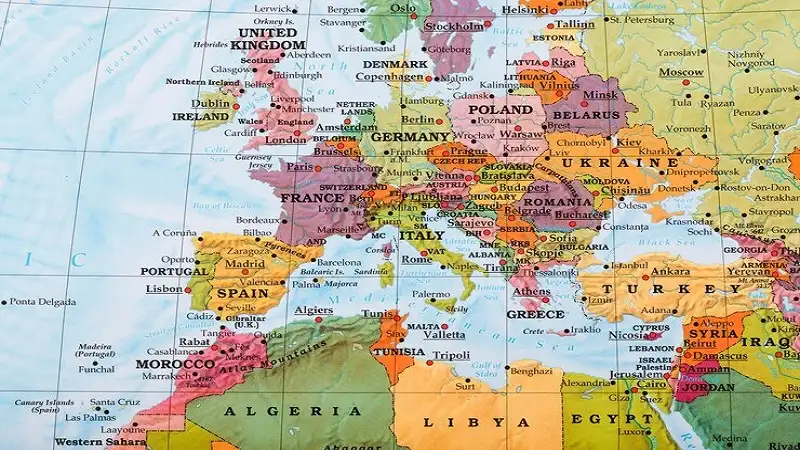
The Labeled:zvxv2jzsbxe= Europe Map is a rich tapestry of history, culture, geography, and politics. From the bustling streets of Paris to the scenic fjords of Norway, Europe is a continent that captivates travelers and scholars alike. In this article, we will explore the various components of a labeled map of Europe, diving deep into its countries, capitals, geographical features, and more.
Understanding the Geography of Europe
Labeled:zvxv2jzsbxe= Europe Map is the second smallest continent, covering about 10.18 million square kilometers. It is bounded by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east. The continent is characterized by diverse geographical features, including mountain ranges, plains, rivers, and lakes.
Major Mountain Ranges
- The Alps: Stretching across eight countries, including France, Switzerland, and Italy, the Alps are the highest mountain range in Europe.
- The Pyrenees: Forming a natural border between France and Spain, the Pyrenees offer stunning landscapes and are a popular destination for hiking and skiing.
- The Carpathians: Located in Central and Eastern Europe, the Carpathians are known for their rugged terrain and natural beauty.
Important Rivers
- The Danube: As the second longest river in Europe, the Danube flows through ten countries, making it a crucial waterway for trade and transport.
- The Rhine: Flowing through Germany and into the Netherlands, the Rhine is a key river for commerce and is lined with picturesque towns and vineyards.
- The Volga: The longest river in Europe, the Volga is essential for Russian navigation and agriculture.
Lakes
- Lake Baikal: Though primarily located in Asia, people cannot overlook Lake Baikal’s significance to Europe as it holds the title of the deepest freshwater lake in the world.
- Lake Geneva: Situated between France and Switzerland, this lake attracts visitors with its stunning views and luxury resorts.
Countries and Capitals of Europe
A labeled map of Labeled:zvxv2jzsbxe= Europe Map is incomplete without highlighting its diverse countries and their capitals. Europe is home to 44 countries, each with its unique identity, history, and culture.
Western Europe
- France (Paris): Known for its art, fashion, and cuisine, Paris is a hub of cultural activity.
- Germany (Berlin): Berlin is a city rich in history, known for its vibrant arts scene and historical landmarks.
- United Kingdom (London): London is a global city known for its finance, culture, and diverse population.
Southern Europe
- Italy (Rome): The capital of Italy, Rome is a treasure trove of ancient history and architecture.
- Spain (Madrid): Spain’s capital, Madrid, is famous for its royal palace and bustling nightlife.
- Greece (Athens): Known as the cradle of Western civilization, Athens is steeped in history and archaeological wonders.
Northern Europe
- Sweden (Stockholm): Known for its stunning archipelago and rich history, Stockholm is a vibrant capital.
- Finland (Helsinki): Helsinki is renowned for its modern design and beautiful coastal landscape.
- Denmark (Copenhagen): Famous for its fairy-tale charm, Copenhagen is a hub for culture and sustainability.
Eastern Europe
- Poland (Warsaw): Warsaw has emerged as a modern city with a rich historical background.
- Ukraine (Kyiv): People know Kyiv, the capital of Ukraine, for its historical sites and vibrant culture.
- Russia (Moscow): Many recognize Moscow, the capital of Russia, for its rich history, cultural heritage, and iconic landmarks like the Kremlin and Red Square.
Cultural Diversity in Europe
Labeled:zvxv2jzsbxe= Europe Map is a melting pot of cultures, languages, and traditions. Each country boasts its unique heritage, contributing to the continent’s rich cultural tapestry.
Languages
- Multilingualism: Europe is home to over 200 languages. Major languages include English, French, German, Spanish, and Italian.
- Minority Languages: Numerous minority languages exist, such as Basque in Spain and Catalan in both Spain and France.
Festivals and Traditions
- Oktoberfest (Germany): This famous beer festival in Munich attracts millions every year.
- Carnival (Venice, Italy): Known for its elaborate masks and costumes, the Venice Carnival is a highlight of Italian culture.
- Bastille Day (France): Celebrated on July 14, Bastille Day commemorates the French Revolution and is marked by fireworks and parades.
Cuisine
- Italian Cuisine: Known for pasta, pizza, and regional dishes like risotto and gelato.
- French Cuisine: Renowned for its sophistication, French cuisine includes specialties like croissants, coq au vin, and cheese.
- Spanish Tapas: Small plates of various dishes that encourage sharing and socializing.
Historical Significance of Europe
Labeled:zvxv2jzsbxe= Europe Map has played a pivotal role in world history, shaping modern civilization through its political, social, and economic developments.
Ancient Civilizations
- Greece: The birthplace of democracy, philosophy, and the Olympic Games.
- Rome: Known for its empire, innovations in law, engineering, and architecture.
The Middle Ages
- Feudalism: The dominant social system in medieval Europe, characterized by the exchange of land for service.
- The Crusades: A series of religious wars that shaped European and Middle Eastern relations.
The Renaissance and Enlightenment
- Renaissance: A period of revival in art, literature, and learning, marking the transition to the modern age.
- Enlightenment: A movement emphasizing reason, individualism, and skepticism of traditional authority, influencing revolutions across the globe.
The World Wars
- World War I: Resulted in significant territorial changes and the establishment of new nations.
- World War II: A devastating conflict that led to widespread destruction and the establishment of the United Nations.
Political Landscape of Europe
Labeled:zvxv2jzsbxe= Europe Map political landscape is complex, marked by a variety of governmental systems and international organizations.
European Union (EU)
- Formation: Established in the aftermath of World War II to foster economic cooperation and prevent future conflicts.
- Member States: Currently comprises 27 member states, facilitating free trade and movement across borders.
Political Systems
- Parliamentary Systems: Many European countries, including the UK and Germany, have parliamentary systems where the government is accountable to parliament.
- Presidential Systems: France has a semi-presidential system, blending elements of parliamentary and presidential systems.
Current Issues
- Brexit: The United Kingdom’s departure from the EU has significant implications for both regions.
- Migration Crisis: Ongoing debates regarding immigration policy and border control are shaping European politics.
- Climate Change: Europe is at the forefront of climate action, pushing for sustainable policies and practices.
The Role of Tourism in Europe
Tourism is a major contributor to Labeled:zvxv2jzsbxe= Europe Map economy, drawing millions of visitors to its cities, historical sites, and natural attractions.
Major Tourist Destinations
- Paris: Known for its iconic landmarks like the Eiffel Tower and Louvre Museum.
- Rome: Attracts visitors with its ancient ruins, including the Colosseum and Roman Forum.
- Barcelona: Famous for its unique architecture by Antoni Gaudí, such as the Sagrada Família.
Ecotourism and Sustainability
- Nature Reserves: Many countries promote ecotourism, focusing on conservation and sustainable practices.
- Cultural Heritage: Efforts are being made to preserve cultural heritage sites while promoting responsible tourism.
Impact of Tourism
- Economic Benefits: Tourism provides jobs and stimulates local economies.
- Cultural Exchange: Travelers contribute to cultural exchange and understanding among different nations.
Future Trends in Europe
As Europe continues to evolve, several trends are shaping its future.
Digital Transformation
- Smart Cities: Urban areas are increasingly adopting technology for sustainable and efficient living.
- E-Government: Many countries are digitizing government services to improve accessibility and efficiency.
Demographic Changes
- Aging Population: Many European countries are facing challenges related to an aging population, impacting healthcare and social services.
- Youth movements increasingly engage younger generations in social issues, as they advocate for climate action and equality.
Global Relations
- Geopolitical Challenges: Various geopolitical challenges, including relations with Russia and China, are testing Europe’s role in global affairs.
- Trade Agreements: The EU is actively seeking new trade partnerships to strengthen its economic position.
Conclusion
A labeled Labeled:zvxv2jzsbxe= Europe Map offers a window into the continent’s rich geography, diverse cultures, and historical significance. From its iconic landmarks to its complex political landscape, Europe is a continent that continues to shape the world. Whether you’re a traveler, a student of history, or simply curious about this fascinating region, understanding the elements of Europe through its map can enhance your appreciation of its many dimensions. As Europe faces future challenges and opportunities, it remains a vital and dynamic part of the global community.Read More infotimedod.